Microbial Metabolomics Analysis
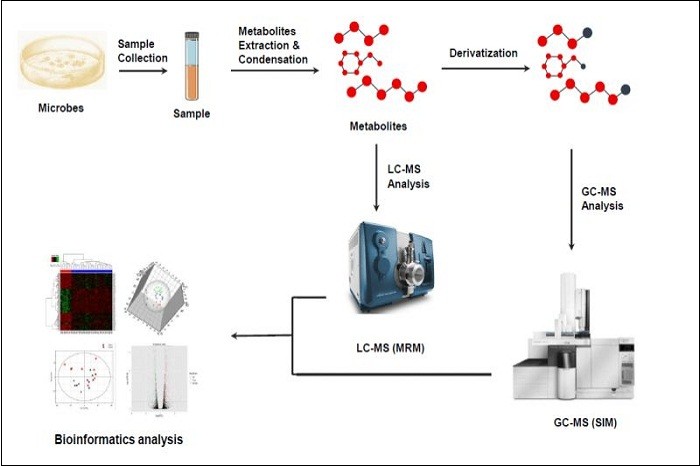
Microbial metabolomics is a study of the complete set of metabolites within a microorganism. Microorganism is a bunch of small creatures which can not be easily identified by naked eyes, and exist in multiple forms, including bacteria, fungi, and some algea, and have the most diverse metabolic characteristics. Each microorganism generally has relatively small genome and proteomes, and the genome and proteome data information are far less than that of the eukaryotes. However, the metabolome of each microorganism is very distinctive, and reflects the cellular activity in a more direct way.
Plant Metabolomics in a Changing World in Plant Genetics and breeding
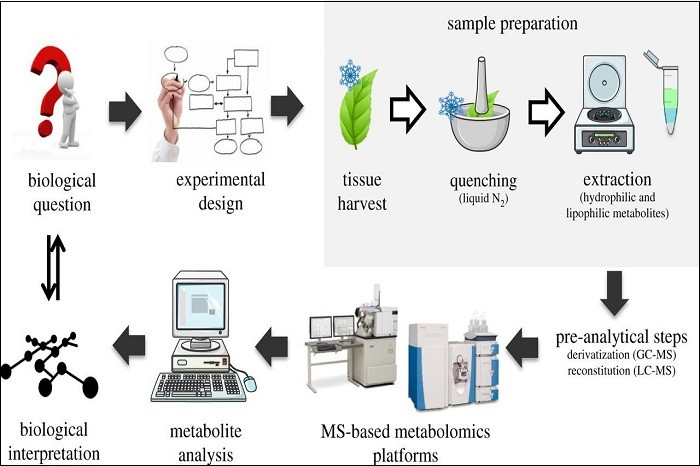
Metabolites are indispensable component of plant metabolism owing to their influence on plant biomass and architecture. In recent years, metabolomics has established itself as one of the major breakthroughs in science, paving the way for accurate metabolite profiling in microbes, plants and animals.
Metagenomics and Metatranscriptomics Bioinformatics Analysis

Metagenomics is the study of genetic material recovered directly from environmental samples. The broad field may also be referred to as environmental genomics, ecogenomics or community genomics.
Metagenomic Next Generation Sequencing in clinical Microbiology
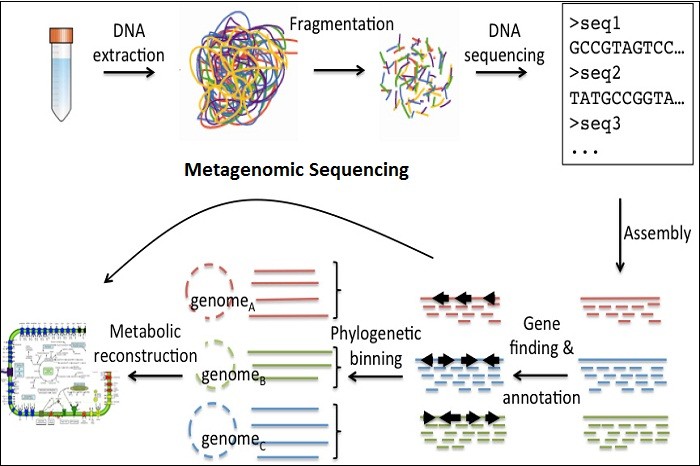
Metagenomics is the study of genetic material recovered directly from environmental samples. The broad field may also be referred to as environmental genomics, ecogenomics or community genomics.
Metabolomics Bioinformatics Analysis

Metabolomics is the scientific study of chemical processes involving metabolites, the small molecule substrates, intermediates and products of metabolism. Specifically, metabolomics is the "systematic study of the unique chemical fingerprints that specific cellular processes leave behind", the study of their small-molecule metabolite profiles.The metabolome represents the complete set of metabolites in a biological cell, tissue, organ or organism, which are the end products of cellular processes.
How Bioinformatics Changing the Biotechnology in World?
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms.Biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life.
Biochemistry and Molecular Biology the Science icon in Biotechnology

Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms.Biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life.